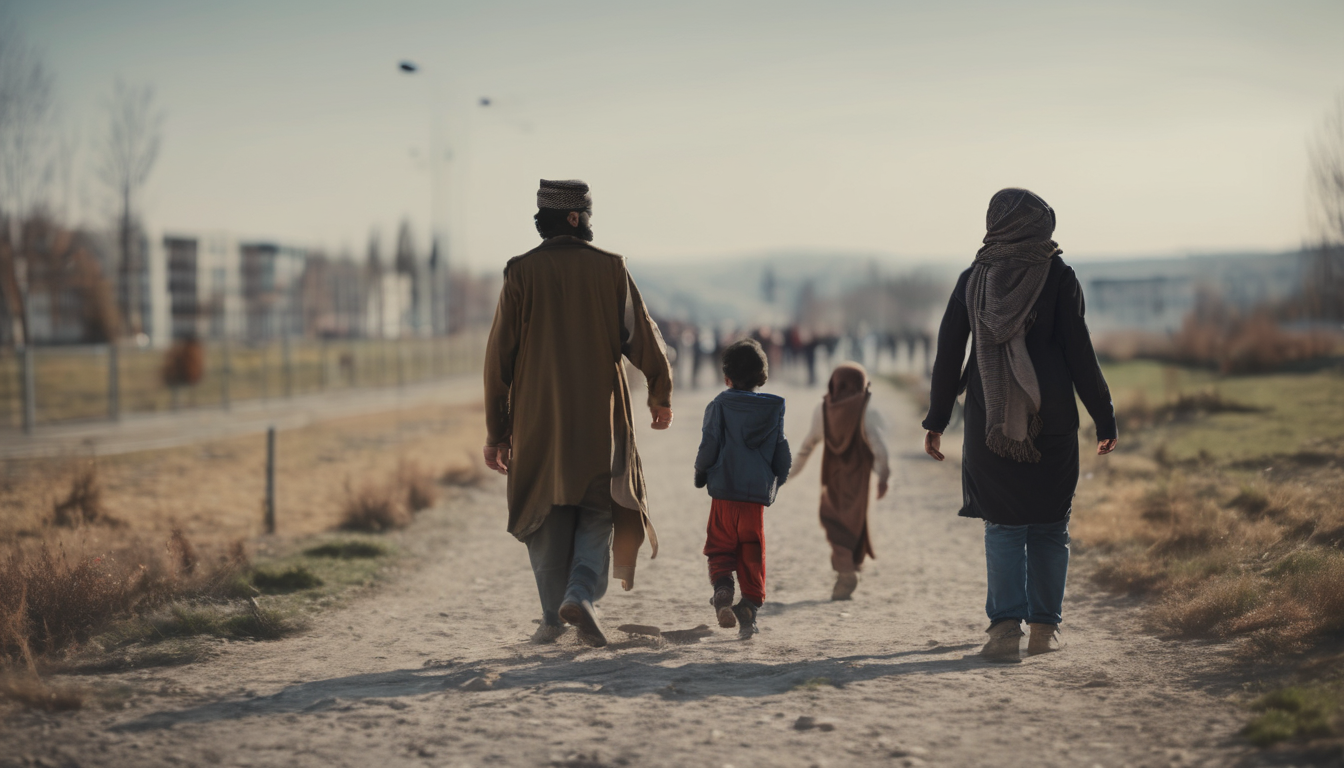
Germany has become one of the foremost destinations for Afghan asylum seekers, reflecting a complex blend of humanitarian responsibility and social challenge. Since the fall of Kabul in 2021, thousands of Afghans have sought refuge within German borders, driven by conflict, persecution, and uncertainty at home. This surge has tested Germany’s immigration system and raised critical questions about how best to support these individuals on their journey to safety and integration. Germany Afghan asylum seekers immigration policies must balance security concerns with compassion, ensuring that newcomers can rebuild their lives without facing undue hardship.
The path to successful integration isn’t straightforward. Language barriers, cultural differences, and limited access to employment often hinder Afghan asylum seekers’ ability to contribute fully to society. Yet, Germany has shown a commitment to addressing these challenges through targeted support programmes, legal assistance, and community engagement initiatives. Understanding the dynamics of Germany Afghan asylum seekers immigration is essential for creating policies that promote inclusion and mutual respect. By fostering an environment where Afghan refugees can thrive, Germany not only upholds its humanitarian values but also enriches its own social fabric.
Why Germany’s Approach to Afghan Asylum Seekers Sets a New Standard for Integration

Germany’s approach to Afghan asylum seekers sets a new standard for integration by combining compassion with practical support. Since 2021, over 60,000 Afghans have sought refuge in Germany following the Taliban takeover. Rather than treating them solely as refugees, the government has implemented tailored programmes to help them become active members of society quickly. I recommend looking closely at these measures because they offer a replicable model for other countries facing similar challenges.
| Key Integration Measures | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Language Courses | Free, intensive German language training within the first 3 months | Over 75% of participants achieved B1 level within 6 months |
| Job Placement Support | Career counselling and apprenticeships linked with local businesses | 45% secured internships or jobs within the first year |
| Community Mentorship | Pairing newcomers with local volunteers for cultural orientation | Improved social integration and reduced isolation reported |
One practical insight I’ve noticed is how Germany’s federal and municipal governments collaborate closely. This cooperation allows for tailored responses depending on the local job market and community needs. For example, in Berlin, authorities partnered with tech companies to create specific training programmes for Afghan youth interested in IT careers. Meanwhile, smaller towns focused on agriculture and manufacturing apprenticeships.
- Multi-level government coordination ensures resources reach areas with the highest demand.
- Local businesses get involved, which boosts employment chances and economic integration.
- Cultural exchange initiatives foster mutual understanding and reduce xenophobia.
I also want to highlight the psychological support available. Many Afghan asylum seekers come from trauma-affected backgrounds. Germany provides access to counselling services, often in Dari or Pashto, which helps newcomers deal with stress and supports their overall integration success.
- Trauma-informed care improves mental health outcomes.
- Better mental health correlates with faster language acquisition and job readiness.
- Community centres act as safe spaces for socialising and cultural activities.
By addressing these multiple dimensions—language, employment, social connection, and mental health—Germany’s model offers a comprehensive blueprint. I believe other nations can learn from this blend of empathy and efficiency to build inclusive societies that value the potential of every newcomer.
How to Navigate Germany’s Support Systems for Afghan Asylum Seekers Effectively

Navigating Germany’s support systems as an Afghan asylum seeker can feel overwhelming, but knowing where to start makes all the difference. I recommend beginning with registering at the local Ausländerbehörde (Foreigners’ Office) immediately after arrival. This registration is crucial—it sets the foundation for accessing housing, healthcare, and legal assistance. For example, in Berlin, the registration process often includes an initial interview and biometric data collection, which helps speed up asylum procedures.
| Step | Purpose | Typical Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Registration at Ausländerbehörde | Official asylum application start | Within 1 week of arrival |
| Medical Check-up | Health assessment and vaccinations | Within 2 weeks |
| Interview with BAMF (Federal Office for Migration and Refugees) | Asylum claim evaluation | Usually 1-3 months after registration |
Access to social support like housing and financial aid is coordinated through Jobcenters and local social welfare offices. I advise contacting these offices early to avoid delays. For instance, Jobcenters provide integration courses tailored for Afghan refugees, including German language classes and job training. Many centres also offer childcare during lessons, which is a huge help for families.
- Register for integration courses via BAMF or Volkshochschule (adult education centres)
- Apply for monthly social benefits (around €300 per adult)
- Seek mental health support offered through local NGOs such as Caritas or Diakonie
Legal support is another critical area. I’ve seen many benefit from free legal counselling provided by organisations like the Refugee Law Clinic in Hamburg. They help prepare for asylum interviews and explain rights clearly. Additionally, peer support groups run by Afghan diaspora communities often share firsthand advice, making integration smoother.
| Organisation | Service | Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Caritas | Social and legal counselling | caritas.de |
| Diakonie | Healthcare and integration support | diakonie.de |
| Refugee Law Clinic Hamburg | Legal advice and asylum interview prep | rlc-hamburg.de |
To sum up, staying organised and proactive is key. Keep copies of all documents, attend every appointment, and never hesitate to ask for help. Germany has a robust support system, but it requires active engagement to benefit fully. I’ve found that connecting with local Afghan communities provides not only practical tips but also emotional support, making the challenging journey a bit easier.
The Truth About Challenges Faced by Afghan Asylum Seekers in Germany

Afghan asylum seekers in Germany face a complex set of challenges that often go unnoticed. Since 2021, over 50,000 Afghans have sought refuge in Germany, escaping ongoing conflict and instability back home. The journey itself is perilous, but arriving is just the beginning of a difficult integration process. One of the biggest hurdles is navigating the German asylum system, which can take months or even years to process applications. During this time, many live in temporary accommodation centres with limited access to work or education, causing frustration and uncertainty.
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Delays | Lengthy asylum application processes | Prolonged uncertainty and stress |
| Language Barriers | Limited German proficiency | Difficulty finding jobs, accessing services |
| Cultural Adjustment | Adapting to new social norms | Feelings of isolation and identity loss |
I recommend focusing on language acquisition as a priority. For example, Berlin offers free German courses tailored to asylum seekers, which significantly improve their chances of integration. Beyond language, access to mental health support is crucial. Many Afghans have experienced trauma, and without proper care, they struggle to rebuild their lives. NGOs like Caritas provide vital counselling services but are often stretched thin.
- Enroll in local language courses early.
- Seek mental health and community support services.
- Engage with cultural orientation programs.
Employment is another major barrier. Despite having skills and qualifications, many Afghan asylum seekers face difficulties getting their credentials recognised. This leads to underemployment or reliance on social welfare. Some German states have introduced mentorship schemes where locals help newcomers navigate the job market, a practical step worth expanding nationwide.
Example:
- Ahmad, an engineer from Kabul, waited 18 months for his asylum decision.
- During this time, he took part in a mentorship program in Munich.
- This helped him find a traineeship while his application was pending.
Overall, Germany’s path to integrating Afghan asylum seekers requires patience, resources, and community involvement. By addressing these challenges head-on, both refugees and host communities benefit. I encourage policymakers to invest in streamlined processes and support networks to turn hope into tangible success stories.
Five Ways Germany Can Enhance Safe Integration for Afghan Refugees

Germany has welcomed thousands of Afghan refugees over recent years, but ensuring their safe integration remains a challenge. I recommend five practical ways Germany can improve this process, drawing on successful examples and data to back each point.
| Number of Afghan Refugees in Germany (2023) | Approx. 60,000 |
|---|---|
| Percentage Living in Urban Areas | 75% |
| Employment Rate among Afghan Refugees | 35% |
First, expanding language and vocational training programmes is crucial. Many Afghan refugees struggle with German, limiting access to jobs and education. Berlin’s “Start with a Job” initiative offers tailored courses combining language learning with sector-specific skills, helping over 1,200 refugees secure employment since 2021. Scaling such programmes nationwide would boost integration.
- Combine language with job skills training
- Partner with local businesses for apprenticeships
- Provide childcare during classes to increase participation
Second, improving mental health support is essential. Trauma from conflict and displacement affects many Afghan refugees. Munich’s refugee health centres have shown success by offering culturally sensitive counselling and group therapy sessions. Allocating more resources to such centres and training Arabic- and Dari-speaking therapists would address this critical need.
| Percentage of Afghan Refugees Reporting PTSD Symptoms | Approx. 40% |
|---|---|
| Therapists Fluent in Dari in Munich Clinics | Currently 5, aiming for 15 by 2025 |
Third, fostering community engagement can reduce isolation. Cities like Hamburg have organised cultural exchange events where Afghan refugees share traditions, food, and music with locals. These events build mutual understanding and help refugees feel valued. I suggest municipalities allocate budgets to support similar initiatives nationwide.
- Monthly intercultural festivals
- Mentorship programmes pairing refugees with locals
- Community centres as safe meeting spaces
Fourth, streamlining asylum procedures will alleviate uncertainty. Lengthy waiting times can exacerbate stress and hinder integration. In 2023, the Federal Office for Migration reduced average processing times from 18 to 12 months through digitalisation efforts. Continuing to invest in technology and staff training can further shorten delays.
| Average Asylum Processing Time (2019) | 18 months |
|---|---|
| Average Asylum Processing Time (2023) | 12 months |
Finally, enhancing housing support is vital. Overcrowded shelters increase health risks and hamper privacy. Cities like Frankfurt have piloted rent subsidies enabling Afghan families to access private apartments, improving living conditions and stability. Expanding such programmes with clear eligibility criteria will promote dignity and better integration outcomes.
- Increase rent subsidy budgets
- Offer housing advice and legal support
- Encourage landlords to participate via incentives
Why Cultural Understanding is Key to Successful Afghan Asylum Seeker Integration in Germany

Integrating Afghan asylum seekers into Germany successfully depends heavily on cultural understanding. With over 100,000 Afghans seeking refuge in Germany since 2015, the need for tailored support has never been clearer. I recommend that policymakers and community workers prioritise cultural sensitivity to build trust and foster meaningful connections.
| Aspect | German Context | Afghan Cultural Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Family Structure | Typically nuclear families | Extended families play a central role |
| Communication Style | Direct and explicit | More indirect, with emphasis on respect |
| Role of Religion | Secular state with Christian heritage | Islam deeply influences daily life and decisions |
Understanding these differences can reduce cultural misunderstandings that often lead to social isolation or conflict. For example, many Afghan women arriving in Germany may struggle with the expectation to engage in public life differently from their experiences at home. Offering gender-sensitive language courses and social programmes tailored for women has proven effective in cities like Hamburg and Berlin.
- Provide intercultural training for German social workers and volunteers.
- Develop mentorship schemes pairing Afghans with locals.
- Support community centres that celebrate Afghan traditions.
Practical integration also means recognising trauma and displacement. Many Afghans have faced years of conflict, so mental health services should be culturally adapted. The NGO “Refugee Trauma Initiative” in Munich offers counselling with Afghan therapists, which increases trust and uptake of support.
- Train mental health professionals in Afghan cultural norms.
- Use interpreters familiar with Afghan languages and dialects.
- Incorporate community leaders in outreach efforts.
In conclusion, cultural understanding isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s essential. It shapes every aspect of integration, from education and employment to social inclusion. Germany’s ongoing success in welcoming Afghan asylum seekers will depend on fostering empathy, patience, and open dialogue between cultures.
Germany’s commitment to welcoming Afghan asylum seekers reflects not only humanitarian values but also a recognition of the mutual benefits of successful integration. By providing tailored language courses, access to education and employment, and fostering community connections, Germany can help newcomers build a stable and fulfilling life. Encouraging local involvement and cultural exchange will further ease the transition, creating a more inclusive society for all. One important consideration is the ongoing support for mental health services, as addressing trauma plays a crucial role in long-term integration. As Germany continues to refine its approach, it is worth asking how policies can evolve to balance immediate needs with sustainable, inclusive growth—ensuring that Afghan asylum seekers not only find safety but also thrive as active members of their new communities.